No products in the cart.
3D printed functional things for your Litter-Robot 3
Your Cart:
$0.00
Subtotal: $0.00
0
Cart
0
No products in the cart.
LR Things LLC is not affiliated or endorsed by Litter-Robot or Automated Pet Care Products LLC. The registered trademarks used on this website belong solely to the companies described.

LR3 D&D Half Guard – 3D Printed
0 customer reviews
Recent Views: 1,415
$31.99Current price is: $31.99.$39.99 Original price was: $39.99.
LR3 D&D Half Guard – 3D Printed
0 customer reviews
Recent Views: 1,415
$31.99Current price is: $31.99.$39.99 Original price was: $39.99.
LR3 D&D Half Guard – 3D Printed
0 customer reviews
Recent Views: 1,415
$31.99Current price is: $31.99.$39.99 Original price was: $39.99.
DENT & DINGED: THESE PRODUCTS ARE FULLY FUNCTIONAL BUT HAVE NOTICEABLE FINISH DEFECTS.
UPDATE! We’ve changed how our clips are made to make them stronger and more durable!
Clips for any Guard will only come in BLACK (regardless of what is pictured).
3D Printed version! This version is porous so it should be sprayed/wiped and not submerged. The filament I use is mostly made of cornstarch and is biodegradable (under the correct conditions). It will one day start to fail if submerged regularly.
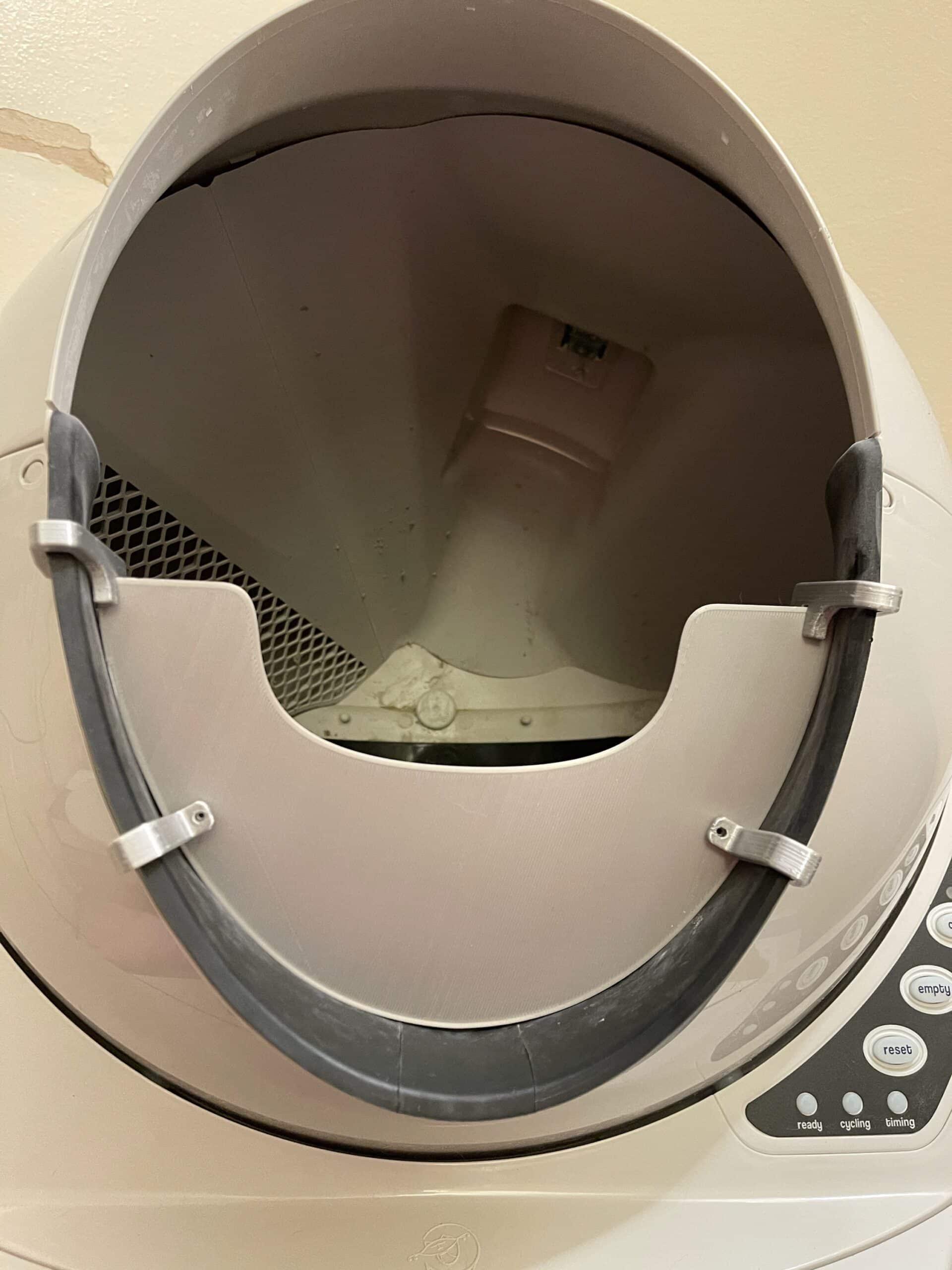
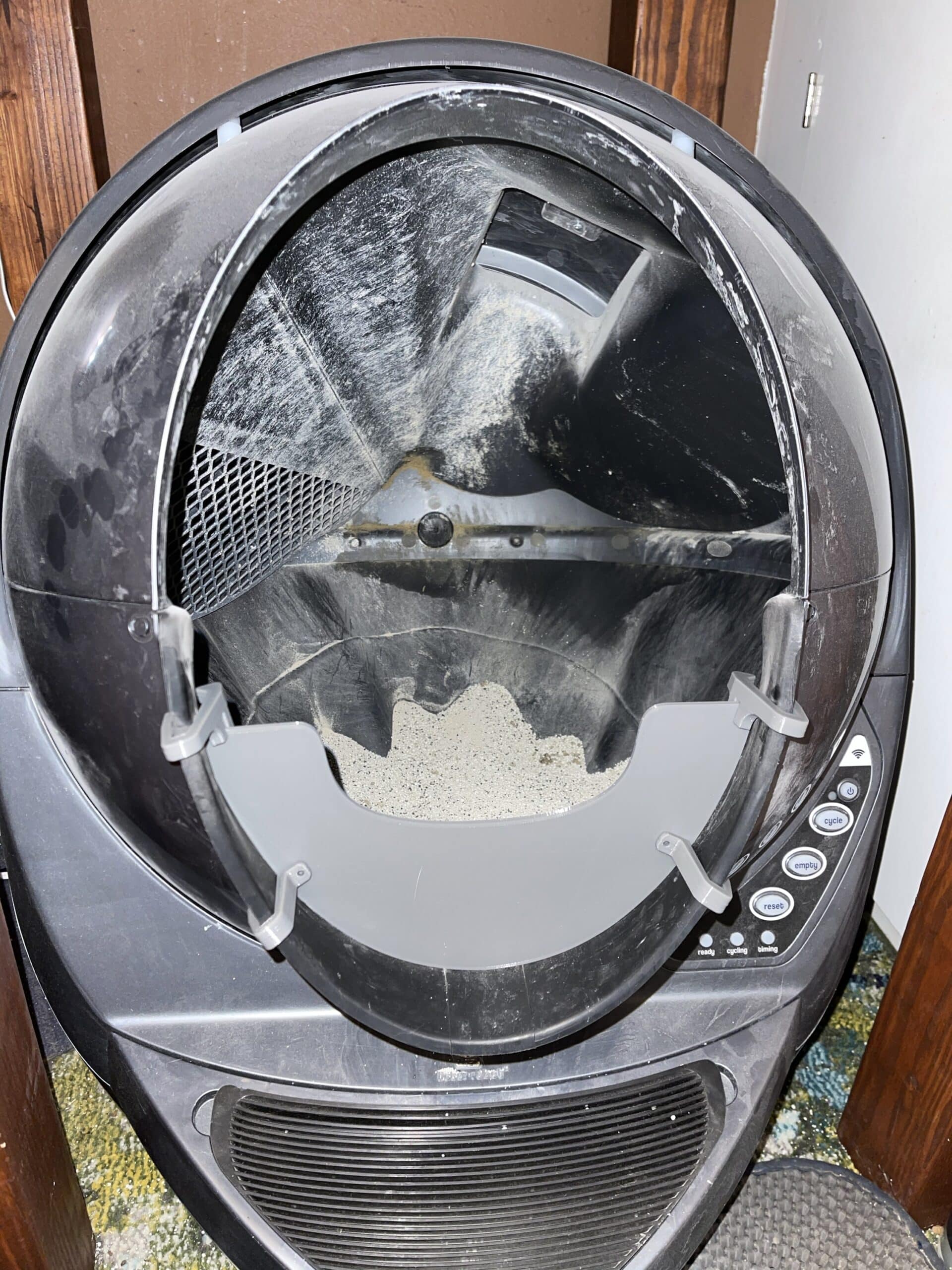
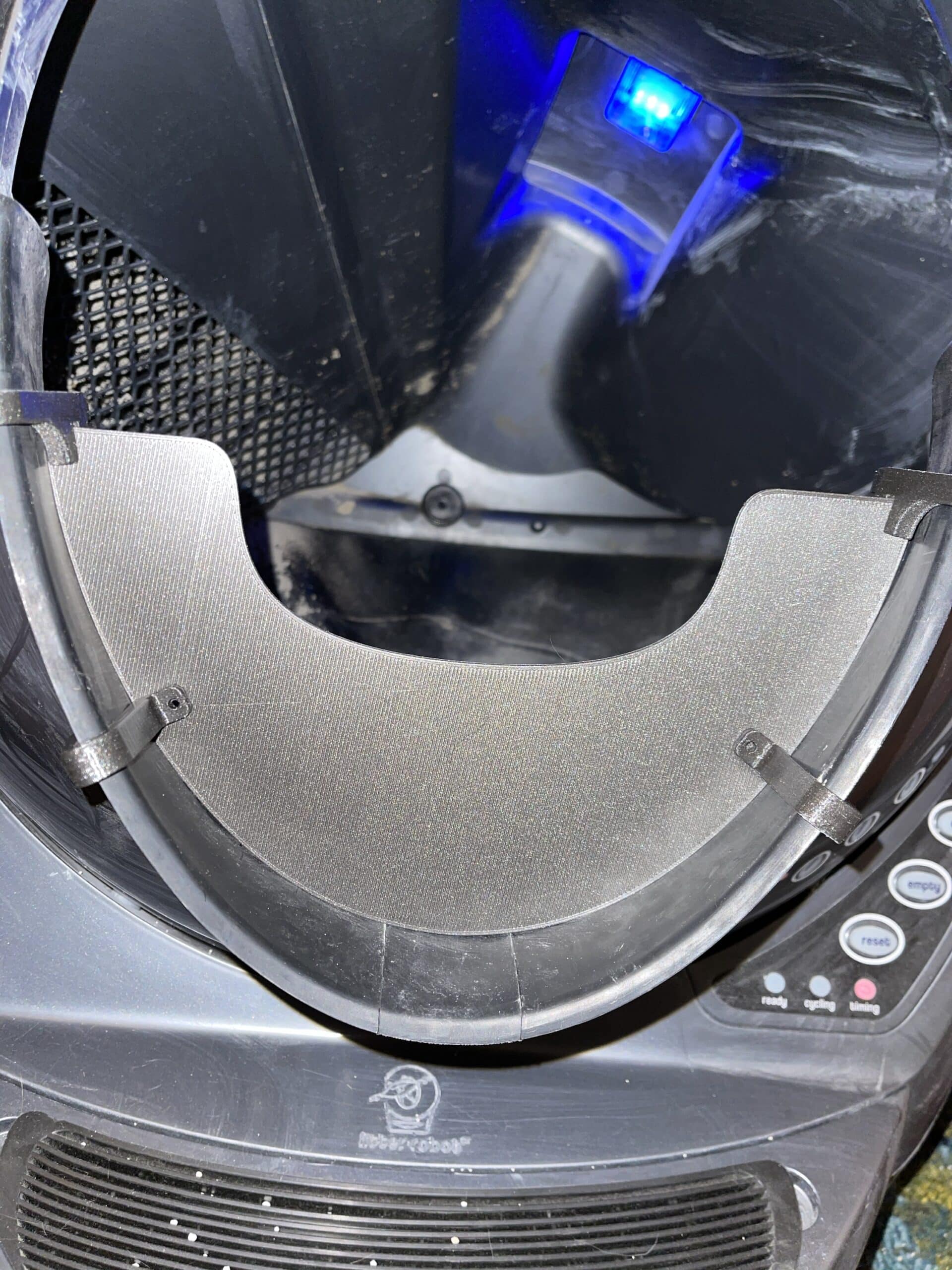
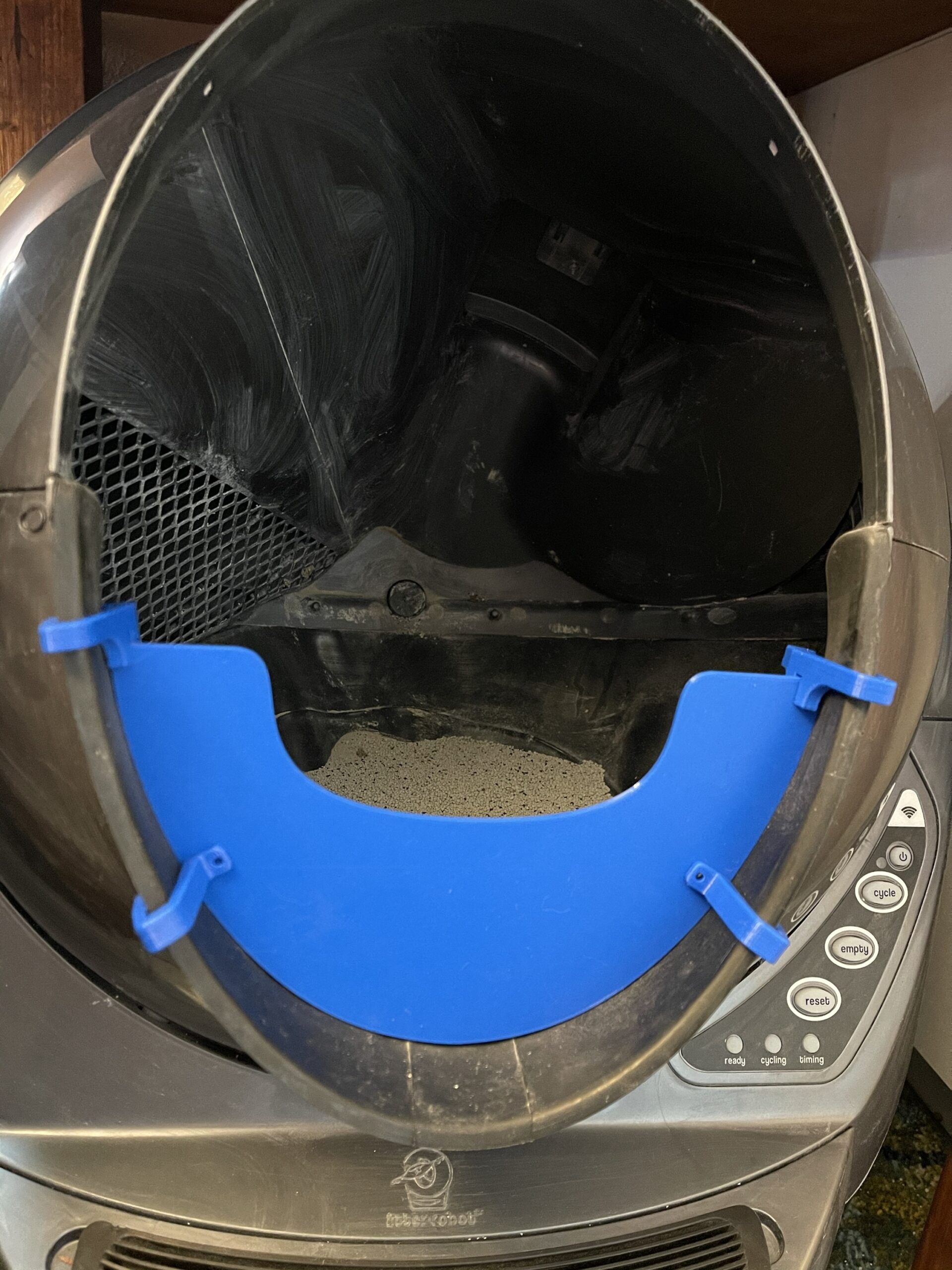
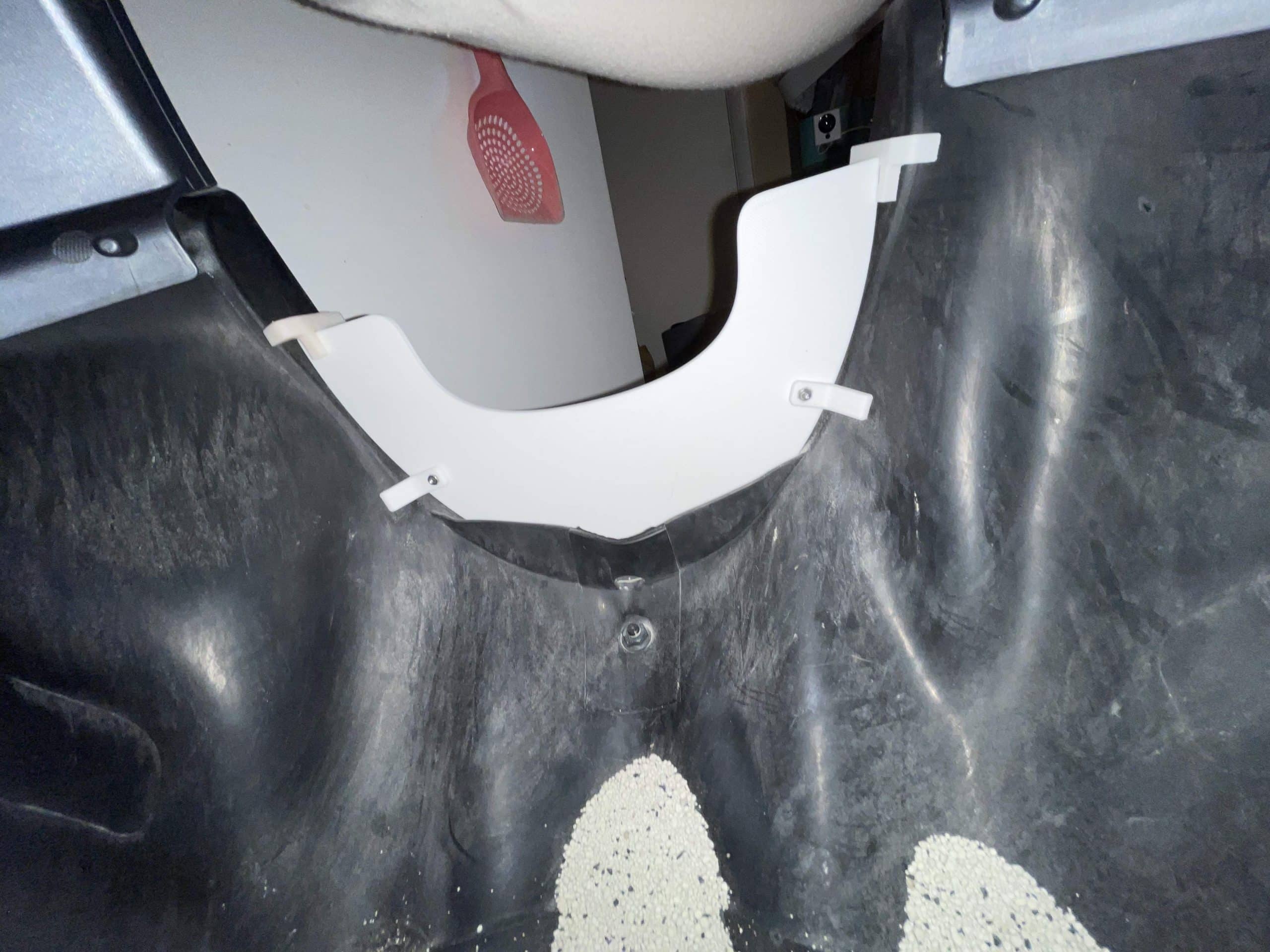
- Our Half Guard is a sturdier and taller solution than Litter-Robot’s Fence and securely attaches to the bottom of the entrance of the Litter-Robot 3 with the provided clips so that even with vigorous pawing it stays in place.
- All Guards help with getting your kitty fully into the LR3 to stop them from hanging their bum’s over the edge of the LR and pooing or peeing outside of the LR3.
- Helps with stopping litter tracking by slowing your cat’s departure from the LR and making them step on the step or stairs to help brush off litter from paws.
- Helps stop your kitty from digging litter out of the LR on to the floor.
- The Half Guard is 3.50″ as measured in the middle of the Guard (LR fence is only 2.5″).
- All clips, screws and nuts are included, install video can be viewed: https://lrt.pet/installguard
Ships in about 2-3.5 weeks default
Color Gallery - View photos of all our color options!This is an aftermarket product made and supported by LR Things and not an original Litter-Robot accessory.
Ships in about 2-3.5 weeks default
Product Description
DENT & DINGED: THESE PRODUCTS ARE FULLY FUNCTIONAL BUT HAVE NOTICEABLE FINISH DEFECTS.
UPDATE! We’ve changed how our clips are made to make them stronger and more durable!
Clips for any Guard will only come in BLACK (regardless of what is pictured).
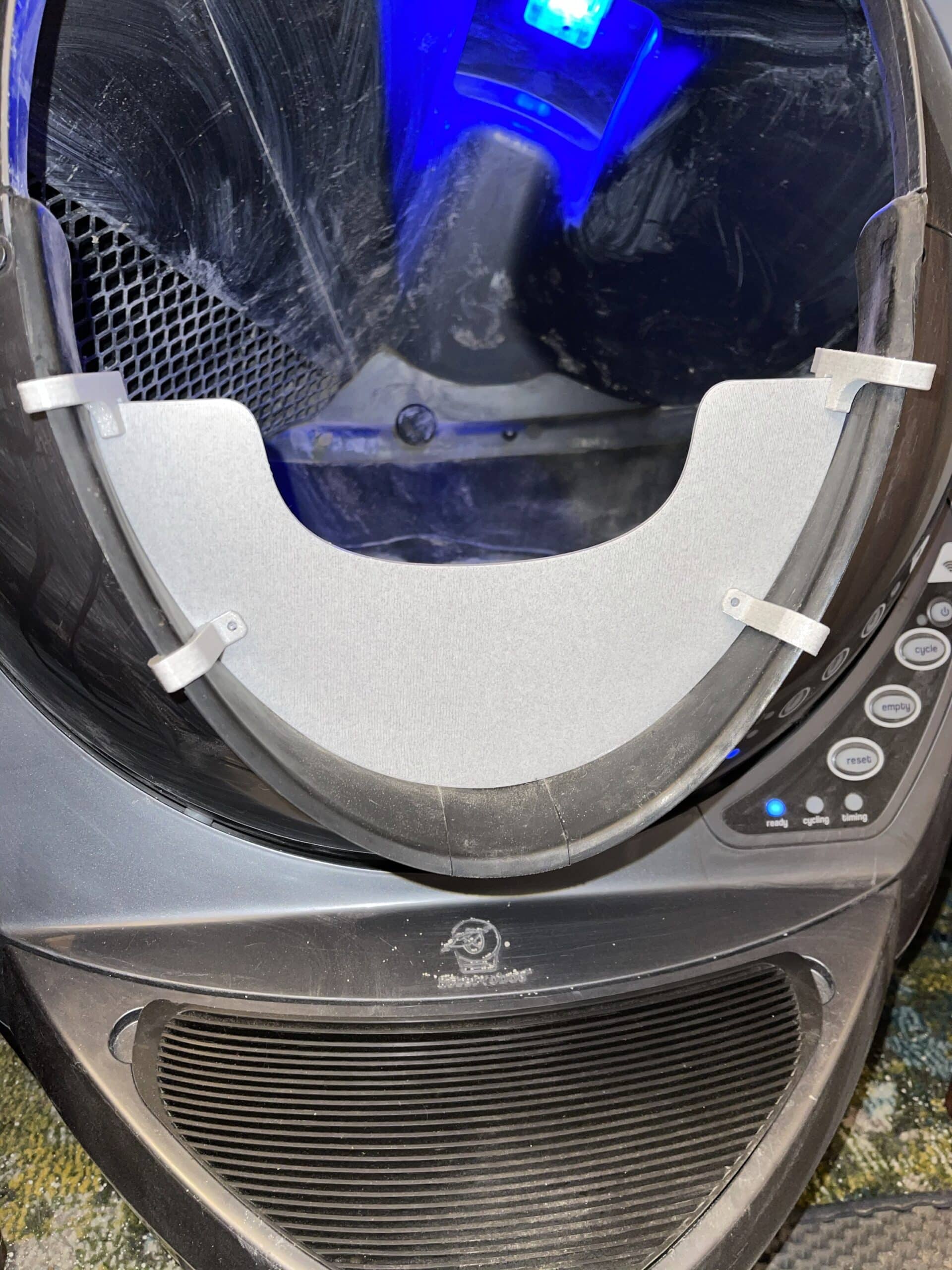
The Half Guard securely attaches to the bottom of the entrance of the Litter-Robot 3 with the provided clips so that even with vigorous pawing it stays in place. The Half Guard is 3.5″ as measured in the middle of the Guard. The sides are taller. FYI the Litter-Robot fence is about 2.5″ tall.
INSTALLATION NOTE: The two bottom clips use screws and nuts, which are included, to attach small stabilizer tabs on the inside of the LR. Just don’t completely tighten those until after they are in place on the LR. Installation video is now available in the photo gallery above!
My orange beast likes to periodically stop by the LR and dig a little litter out for good measure, since installing the Half Guard this has prevented him from getting any out, it’s quite entertaining for me to watch him try though! If you’ve got a real overachiever there is a Full Guard that is 5.75″ tall.
DESIGN NOTE: The original design for the Half Guard was graciously shared by jasonatepaint on Thingiverse.
Be the first to review “LR3 D&D Half Guard – 3D Printed” Cancel reply
How does 3D printing work?
Every 3D printer builds parts based on the same main principle: a digital model is turned into a physical three-dimensional object by adding material a layer at a time. This where the alternative term Additive Manufacturing comes from.
3D printing is a fundamentally different way of producing parts compared to traditional subtractive (CNC machining) or formative (Injection molding) manufacturing technologies.
In 3D printing, no special tools are required (for example, a cutting tool with certain geometry or a mold). Instead the part is manufactured directly onto the built platform layer-by-layer, which leads to a unique set of benefits and limitations
From here, the way a 3D printer works varies by process. For example, desktop FDM printers melt plastic filaments and lay it down onto the print platform through a nozzle (like a high-precision, computer-controlled glue gun). Large industrial SLS machines use a laser to melt (or sinter) thin layers of metal or plastic powders.
The available materials also vary by process. Plastics are by far the most common, but metals can also be 3D printed. The produced parts can also have a wide range of specific physical properties, ranging from optically clear to rubber-like objects.
Depending on the size of the part and the type of printer, a print usually takes about 4 to 18 hours to complete. 3D printed parts are rarely ready-to-use out of the machine though. They often require some post-processing to achieve the desired level of surface finish. These steps take additional time and (usually manual) effort.
This was copied from 3DHubs, for more information please visit them!
Additional Information
| Weight | 0.3125 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 10 × 7 × .25 in |













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.